Insulin is a very important hormone which is secreted by pancreas. One of its main roles is to help cells using glucose as an energy source.
See more about insulin action: INSULIN
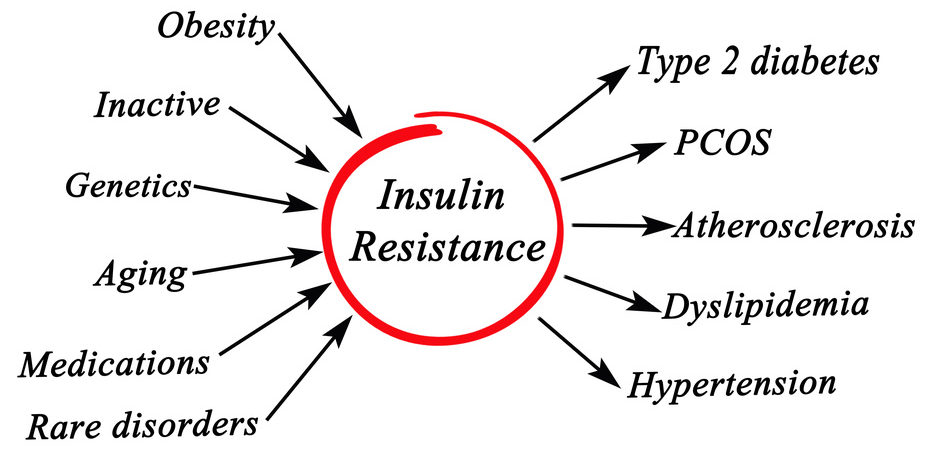
Insulin resistance means that cells ignore insulin's action.
The body turns on compensative mechanisms in order to give cells energy and to avoid accumulation of unused sugar in the blood. This mechanism means to intensify insulin release from pancreas to overlay cell's insensitivity. But here begin another problems due to hyperinsulinemia.
- Elevated insulin level can cause conditions, such as:
- Obesity
- disorders of lipid metabolism
- atherosclerosis
- elevated blood pressure
- polycystic ovarian syndrome
- infertility
This list may continue. If genetic susceptibility and certain environmental factors are present, hard work can cause exhaustion of pancreas and decrease insulin release. This leads rising blood sugar level and developing prediabetes and type 2 diabetes.
Prediabetes includes the diagnosis of decreased glucose tolerance and/or impaired fasting glucose. During these conditions blood glucose level is high than normal but still not in diabetes range.
- The main risk factors for developing insulin resistance are:
- being overweight or obesity, especially when fat is mostly accumulated in belly area
- უმოძრაო ცხოვრების წესი;
- არასწორი კვების რეჟიმი;
- არასრულფასოვანი ძილი;
- თამბაქოს მოხმარება.
Due to modern lifestyle the incidence of metabolic diseases including insulin resistance is markedly increased already from younger age and among children too.
- Insulin resistance have no symptoms itself, but over time it causes a serious complications, such as:
- უშვილობა;
- გულ-სისხლძარღვთა სისტემის დაავადებები;
- შაქრიანი დიაბეტი ტიპი 2.
- The treatment of insulin resistance must include neutralization of it's risk factors. So the plan is:
- ჯანმრთელი დაბალანსებული კვების რეჟიმი და სხეულის მასის შემცირება;
- ფიზიკური აქტივობის გაზრდა;
- ძილის რეჟიმის მოწესრიგება;
- თამბაქოზე უარის თქმა.
Insulin resistance and obesity
There is such a tight connection between insulin resistance and obesity, that it's hard to tell which of them begins first.
It's established that increasing fat tissue volume can cause developing or worsening insulin resistance. And the processes that begin due to insulin resistance including hyperinsulinemia are provocative for developing obesity.
როგორც დადგინდა, დიდი მნიშვნელობა აქვს ჭარბი ცხიმის განაწილების ადგილს და სიმსუქნის შეფასების საყოველთაოდ მიღებული ერთეული _ სხეულის მასის ინდექსი არ არის საკმარისი მაჩვენებელი ინსულინ რეზისტენტობის რისკის შესაფასებლად. ამ შემთხვევაში წამყვანი კრიტერიუმია ცხიმის უპირატესი დაგროვება მუცლის მიდამოში, რადგან ამ ლოკაციაზე ის მეტაბოლურად გაცილებით უფრო აქტიურია, ვიდრე პერიფერიაზე არსებული კანქვეშა ცხიმი. ამიტომ, ინსულინრეზისტენტობის რისკის შეფასების მთავარ კრიტერიუმად მიიჩნევა სწორედ წელის გარშემოწერილობა, როდესაც ის აღემატება მამაკაცებში _ 102 სმ-ს, ხოლო ქალის შემთხვევაში _ 88 სმ-ს.
So the normal BMI doesn't exclude presence of insulin resistance.
The main part of obesity treatment must be detecting insulin resistance, because it's very difficult to loose weight when hyperinsulinemia is present.
The diagnostic test for insulin resistance
Insulin sensitivity can be estimated by the Homeostasis Model Assessment or HOMA index. For calculation of HOMA the following is needed:
- Fasting levels of insulin and glucose must be determined in venous sample;
- These results are used in the formula: HOMA IR=( glucose (mmol/L ) X insulin (mU/L)) / 22.5 X insulin - (mU/L)) / 22,5
The normal range for HOMA IR is between 0.5 - 1.4.
- HOMA IR 1,4-1,9 – points to mild changes
- HOMA IR 2.0-2.9 – points to early insulin resistance
- HOMA IR more than 3.0 - is a sign of marked insulin resistance.
Glucose and insulin tests for HOMA index calculation is performed in the morning in a fasting state - minimum 8 hours after the last meal.



